How do vitamins K and D work together to provide health benefits?
Vitamin D has been found to support bone heath and a well-functioning cardiovascular system. Vitamin D is also often overlooked when it comes to its effects on the immune system. Studies have demonstrated that those with healthy vitamin D levels had a lesser instance of respiratory infections than those with sufficient levels, even after adjusting for variables such as gender, age, season and race. But to get the greatest results from taking Vitamin D, you also need Vitamin K.
Vitamin D promotes the production of vitamin K-dependent proteins (VKDPs), which serve essential roles in bone growth and the vascular system. Vitamin K is necessary for carboxylation, a chemical alteration, of two specific VKDPs: osteocalcin and matrix Gla protein (MGP).
According to the International Journal of Endocrinology, carboxylation of MGP helps to mitigate calcium buildup in blood vessels, supporting a healthy cardiovascular system. Osteocalcin carboxylation supports bone density, a key factor in minimizing the likelihood of future bone issues.
Studies have also shown that taking vitamins D and K together results in lower levels of uncarboxylated osteocalcin and increased bone density. This demonstrates that the vitamin duo is more effective in supporting bone health than supplementing with vitamins D or K alone.
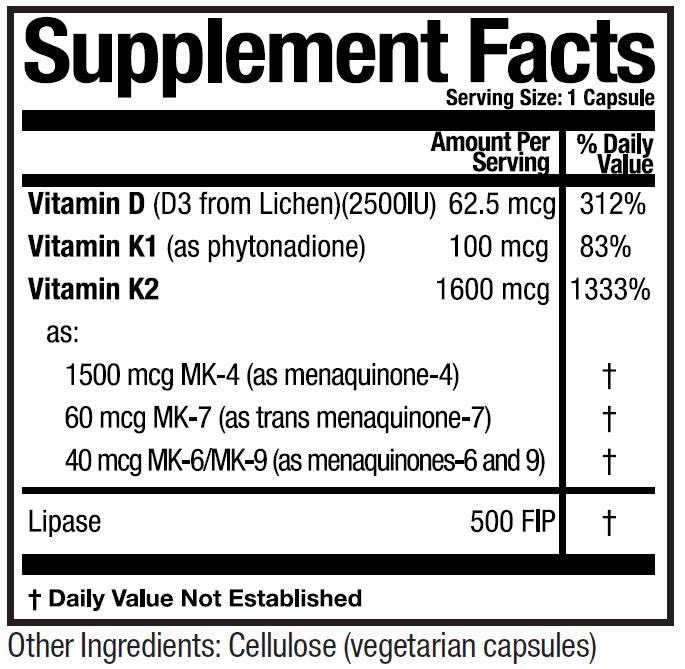
To ensure bioavailability of both vitamins D and K, your body needs enough of the enzyme lipase to properly assimilate these fat-soluble vitamins. Thankfully, KD Ultra contains it all!
What is the difference between vitamin D2 and vitamin D3?
These two forms of vitamin D were thought to be equivalent, however, that is far from the truth. Vitamin D2, or ergocalciferol, is inexpensive to produce and almost always what is found in fortified foods. It is actually less potent and has a shorter duration of action than its Vitamin D3 counterpart known as cholecalciferol.
What are the different forms of vitamin K2?
Vitamin K2 refers to a group of compounds known scientifically as menaquinones (MKs). Several different forms of vitamin K2 exist, ranging from MK4 to MK13, and each provides unique health benefits. The number following the MK refers to the length of the “chain” in its chemical composition (e.g. MK4 is a 4-chain K2). MK4 is most commonly found in the Western diet while high levels of MK7 are found in the Japanese food natto.
KD Ultra includes all four of the currently available supplemental forms of vitamin K2: MK4, MK6, MK7 and MK9. Most products contain only one menaquinone form of K2.
What is lipase?
Lipase is a crucial enzyme that helps break down ingested fats. Without enough lipase, fats cannot be broken down and absorbed properly by the body. This leads to decreased absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, creating deficiencies. The importance of lipase in the fat ingestion process is why we added it to the KD Ultra formula. Both Vitamin K and Vitamin D are fat-soluble vitamins, meaning they dissolve in fats. While water-soluble vitamins dissolve in water and readily absorb into the body, fat-soluble vitamins cannot, which is where enzymes like lipase come in.